异硫氰酸荧光素(Fluorescein isothiocyanate,FITC)抗体
2023.07.13
异硫氰酸荧光素(Fluorescein isothiocyanate,FITC),是荧光素的衍生物, 易溶于水和酒精溶剂, FITC纯品常温常压下为黄色或橙黄色结晶粉末,性质稳定。FITC一种荧光染料,分子量为389.4,吸收光波长为490~495nm,发射光波长为520~530nm,呈现明亮的黄绿色荧光。
FITC 由于其高吸收性,出色的荧光量子产率和良好的水溶性而成为生物学中广泛使用的一种绿色荧光素衍生物之一。FITC 的异硫氰酸酯基与蛋白质或抗体分子中的胺,巯基,咪唑基,酪氨酰基或羰基基团结合,从而实现包括抗体,凝集素在内的蛋白标记。除了用作蛋白质标记物,还可用作蛋白质荧光示踪剂,标记抗体用以快速鉴定病原体,以及用于蛋白质和多肽(HPLC)的微量测序。
Fluorescence microscopy of nanoparticles-fluorescein isothiocyanate (NPs-FITC) and NPs(FITC) in solution. The sizes for the two types of particles are 212 nm (magnification 600×).
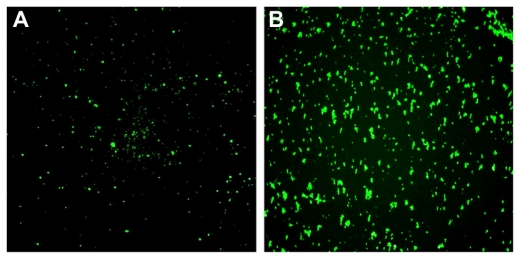
FITC(异硫氰酸荧光素)能与各种抗体蛋白结合,结合后的抗体不丧失与一定抗原结合的特异性。fitc偶联的抗体与待测抗原反应形成抗原-抗体复合物,该复合物上带有fitc标记,通过对fitc发光的检测,则可以快速、准确的检测出待测抗原。fitc也易与抗原结合,标记率高,fitc偶联的抗原也同理地可与待测抗体反应,形成抗原-抗体复合物,从而实现对抗体的检测。
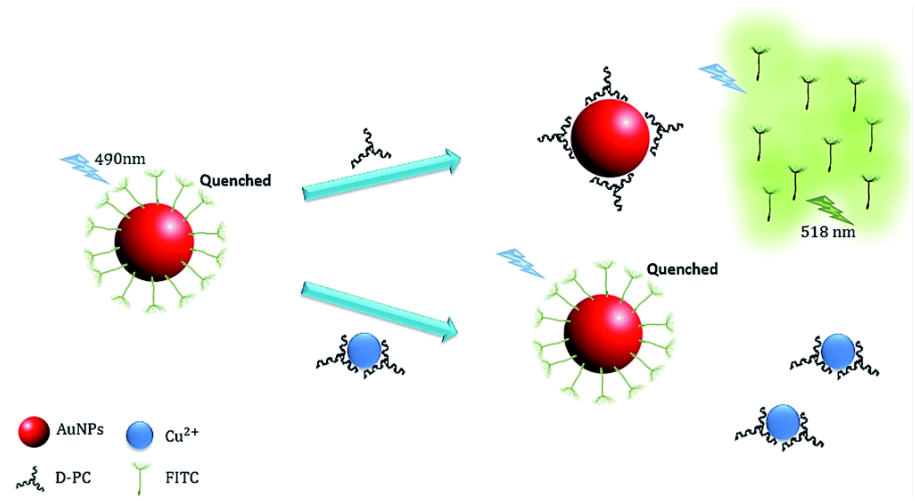
FITC (fluorescein isothiocyanate) is a fluorochrome dye that absorbs ultraviolet or blue light causing molecules to become excited and emit a visible yellow-green light. This emission ceases upon removal of the light causing the excitation. Fluorochrome labeling provides rapid, accurate localization of antigen-antibody interaction when one of the reactants is part of a cell, tissue or other biological structure. FITC is a commonly used marker for antibodies in immunofluorescent techniques since the conjugation of FITC to proteins is relatively easy and does not, in general, destroy the biological activity of the labeled protein. FITC is widely used as a hapten to label different proteins. Applications: Suitable for use in ELISA and Western Blot
Fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC) is the most widely used fluorescent probe for the preparation of conjugates with biological molecules (Hansen, 1967; Haugland, 1990). This xanthene dye (Fig. 1) is particularly useful for several reasons: conjugates are easily prepared because of the water solubility of FITC; it is brightly fluorescent because of its reasonably large extinction coefficients and high quantum yields after conjugation (Table I); and it has low nonspecific binding with most biological tissues. The preparation of fluorescein conjugates from the closely related (4,6-dichlorotriazinyl) aminofluorescein (DTAF) has been recommended because of its higher purity and stability (Blakeslee and Baines, 1976). Typically, three to five fluoresceins can be conjugated to each IgG antibody before self-quenching and altered binding affinities are observed. Fluorescein is maximally excited by blue light and emits primarily green to yellow fluorescence (Fig. 2). Although the excitation spectrum of fluorescein does not overlap with any of the intense emission peaks of mercury arc lamps (313, 334, 365, 405, 435, 546, and 578 nm), the output intensity in the range of 450 to 500 nm is sufficient for the excitation of fluorescein by conventional fluorescence microscopy. The 488-nm line of the argon ion laser used in flow cytometry and LSCM is ideally suited for near-maximal excitation of fluorescein.
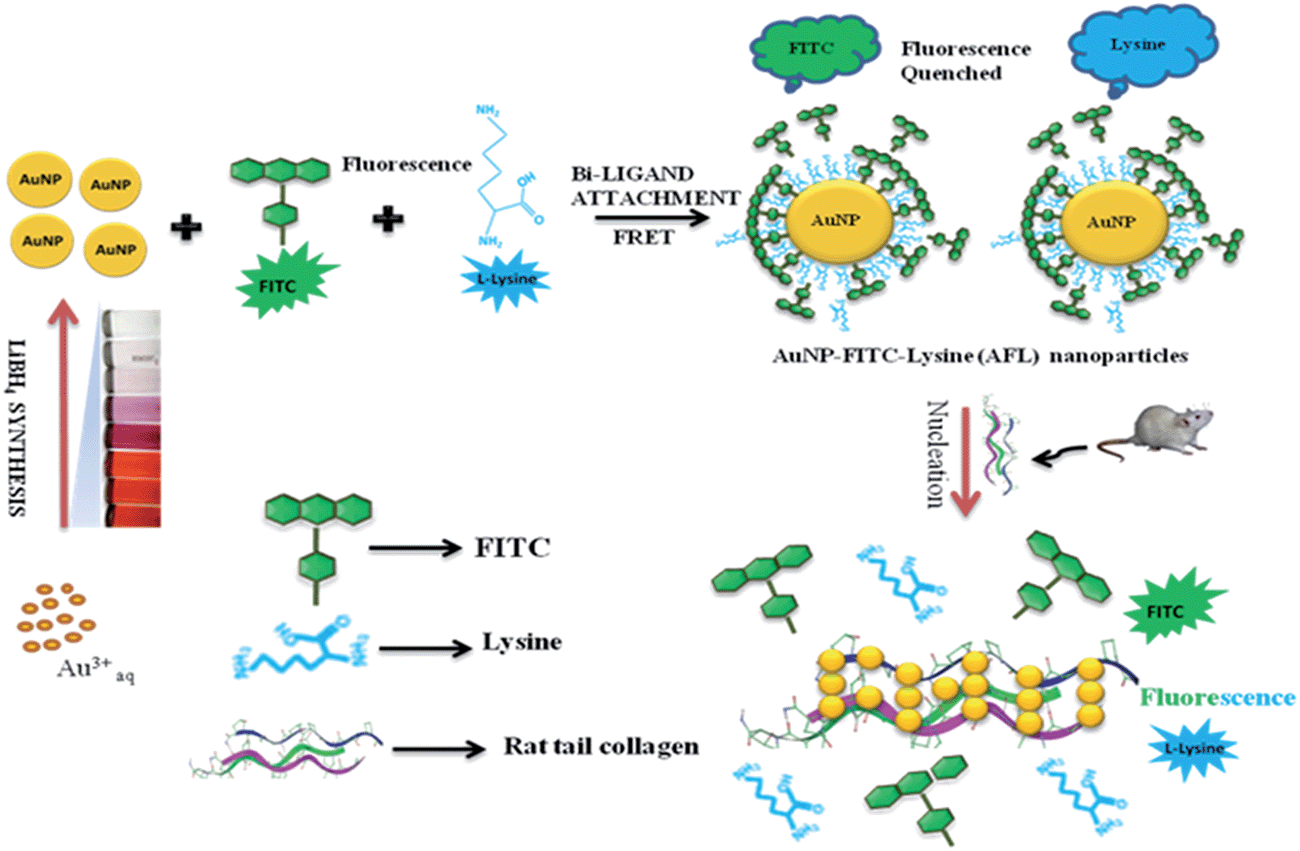
Schematic representation showing LiBH4 synthesized AuNPs, bi-ligand surface modified AuNPs with FITC (Ex/Em: 488/520) and lysine (Ex/Em: 355/∼435) for the formation of AFL nanoparticles, and the fluorometric estimation of rat tail collagen by the induction of FITC and lysine fluorescence from AFL nanoparticles. The release and restored fluorescence of FITC and lysine were attributed to the controlled nucleation of the AFL nanoparticles with collagen.


